NoteNote that with this architecture, the I/O expansion card on each blade server must be compatible with the I/O modules installed in Bay 3 and Bay 4.
Each network interface controller (NIC) has a dedicated channel on the midplane connecting it to a specific I/O module bay. Typically, the integrated NICs are Gigabit Ethernet by default, while the I/O expansion card supports host bus adapters (HBA), host channel adapters (HCA), or Gigabit Ethernet NICs.
Figure 3-2System A Internal Blade Server Connectivity
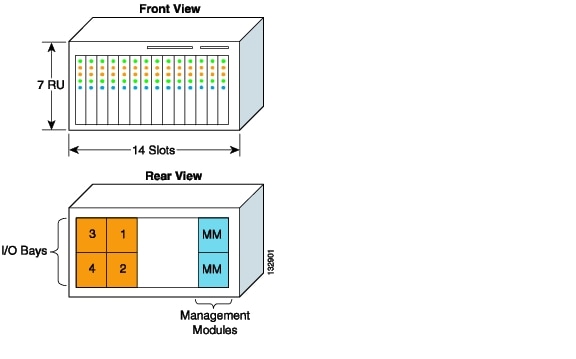
System A is seven rack units (RUs) in height and provides 14 slots to house individual blade servers. The rear of the chassis allows for four individual I/O modules for network connectivity and two management modules to administer the blade system. The blade servers and I/O modules communicate over a midplane, as shown in .
Figure 3-1Example Blade Server Architecture—System A
System A in illustrates the front and rear view of a typical blade server chassis.
•System B—Passes the blade server signaling to the external network port-to-port.
•System A—Uses octopus cabling to interconnect the blade servers with the data center architecture.
Currently, there is no industry-standard design for blade servers or blade server enclosures. Various blade system architectures are available from various vendors. The following section describes two generic blade server systems, which illustrate many of the design features found in these various architectures:
This chapter focuses on integrating blade server systems within the Cisco Data Center Architecture using pass-through technology, which allows individual blade servers to communicate directly with resources external to the blade chassis. Both copper and optical pass-through modules are available that provide access to the blade server controllers. It is therefore important to understand the internal connectivity provided by the blade server chassis before discussing the external ramifications of pass-through deployments.
Each of these I/O technologies provides a means of network connectivity and consolidation.
•Blade Server Chassis Pass-through Modules
•Infiniband switches (such as the Cisco Server Fabric Switch)
•Built-in Ethernet switches (such as the Cisco Ethernet Switch Modules)
A primary consideration in any blade server deployment is how the blade server system is connected to the data center network. There are several I/O options for blade server systems, including the following:
A blade server is an independent server that includes an operating system, memory, one or more processors, network controllers, and optional local storage. Blades servers are designed to reduce the space, power, and cooling requirements within the data center by providing these services within a single chassis. Blade server systems are a key component of data center consolidation that help reduce costs and provide a platform for improving virtualization, automation, and provisioning capabilities.
Blade Servers and Pass-Through Technology
This chapter provides best design practices for deploying blade servers using pass-through technology within the Cisco Data Center Networking Architecture, describes blade server architecture, and explores various methods of deployment. It includes the following sections:
Data Center Blade Server Integration Guide
Data Center Blade Server Integration Guide - Pass-Through Technology [Data Center Designs: Server Networking] - Cisco Systems
Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий